Hallmarks of Aging: Difference between revisions
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="text-align:center;" |[[File:DNA Structure+Key+Labelled.pn NoBB.png|frameless|76x76px]] | | style="text-align:center;" |[[File:DNA Structure+Key+Labelled.pn NoBB.png|frameless|76x76px]] | ||
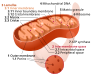
| '''Genomic instability''' | | style="background-color:hsla(180, 100%, 75%);" |'''Genomic instability''' | ||
| Accumulation of DNA damage over time leading to cellular dysfunction. | | style="background-color:hsla(180, 100%, 75%);" |Accumulation of DNA damage over time leading to cellular dysfunction. | ||
| rowspan="5" |'''Primary Hallmarks''' | | rowspan="5" |'''Primary Hallmarks''' | ||
(causes damage) | (causes damage) | ||
| rowspan="6" |Molecular | | rowspan="6" |Molecular | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style="text-align:center;" |[[File:Telomeres transparent.png|frameless|88x88px]] | | style="text-align:center;" |[[File:Telomeres transparent.png|frameless|88x88px]] | ||
| '''Telomere attrition''' | | style="background-color:hsla(180, 100%, 75%);" |'''Telomere attrition''' | ||
| Reduction in the length of telomeres leading to cellular aging. | | style="background-color:hsla(180, 100%, 75%);" |Reduction in the length of telomeres leading to cellular aging. | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style="text-align:center;" |[[File:Epigenome-transparent-upscale.png|frameless|85x85px]] | | style="text-align:center;" |[[File:Epigenome-transparent-upscale.png|frameless|85x85px]] | ||
| '''Epigenetic alterations''' | | style="background-color:hsla(180, 100%, 75%);" |'''Epigenetic alterations''' | ||
| Changes in DNA methylation and histone modification affecting gene expression. | | style="background-color:hsla(180, 100%, 75%);" |Changes in DNA methylation and histone modification affecting gene expression. | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style="text-align:center;" |[[File:Spinach (RNA).jpg|frameless|75x75px]] | | style="text-align:center;" |[[File:Spinach (RNA).jpg|frameless|75x75px]] | ||
|'''Splicing dysregulation''' | | style="background-color:hsla(180, 100%, 75%);" |'''Splicing dysregulation''' | ||
'''(Dysregulation in RNA splicing)''' | '''(Dysregulation in RNA splicing)''' | ||
|Impaired RNA construction from DNA, leading to cellular dysfunction. | | style="background-color:hsla(180, 100%, 75%);" |Impaired RNA construction from DNA, leading to cellular dysfunction. | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style="text-align:center;" |[[File:Stress signaling.png|frameless|95x95px]] | | style="text-align:center;" |[[File:Stress signaling.png|frameless|95x95px]] | ||
| '''Loss of proteostasis''' | | style="background-color:hsla(210, 100%, 75%);" |'''Loss of proteostasis''' | ||
| Disruption in protein folding and stability leading to cell damage. | | style="background-color:hsla(210, 100%, 75%);" |Disruption in protein folding and stability leading to cell damage. | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style="text-align:center;" |[[File:Macro-micro-autophagy.gif|frameless|101x101px]] | | style="text-align:center;" |[[File:Macro-micro-autophagy.gif|frameless|101x101px]] | ||
|'''Compromised autophagy''' | | style="background-color:hsla(210, 100%, 75%);" |'''Compromised autophagy''' | ||
|Impaired cellular maintenance through the consumption of own components. | | style="background-color:hsla(210, 100%, 75%);" | Impaired cellular maintenance through the consumption of own components. | ||
| rowspan="4" |'''Antagonistic Hallmarks''' | | rowspan="4" |'''Antagonistic Hallmarks''' | ||
(responses to damage) | (responses to damage) | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style="text-align:center;" |[[File:Aiga restaurant knife-fork crossed.png|frameless|75x75px]] | | style="text-align:center;" |[[File:Aiga restaurant knife-fork crossed.png|frameless|75x75px]] | ||
|'''Deregulated nutrient sensing''' | | style="background-color:hsla(0, 100%, 75%);" |'''Deregulated nutrient sensing''' | ||
| Alterations in nutrient sensing pathways affecting metabolism and aging. | | style="background-color:hsla(0, 100%, 75%);" | Alterations in nutrient sensing pathways affecting metabolism and aging. | ||
| rowspan="8" |Cellular & Organismal | | rowspan="8" |Cellular & Organismal | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style="text-align:center;" |[[File:Mitochondrion mini.svg|frameless|92x92px]] | | style="text-align:center;" |[[File:Mitochondrion mini.svg|frameless|92x92px]] | ||
|'''Mitochondrial dysfunction''' | | style="background-color:hsla(0, 100%, 75%);" |'''Mitochondrial dysfunction''' | ||
| Decrease in mitochondrial efficiency and increase in oxidative stress. | | style="background-color:hsla(0, 100%, 75%);" | Decrease in mitochondrial efficiency and increase in oxidative stress. | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style="text-align:center;" |[[File:DALL·E 2023-10-15 05.28.43 - Photo of senescent cells magnified under a microscope, showing their characteristic enlarged and flattened morphology. The cells are stained with a bl.png|frameless|75x75px]] | | style="text-align:center;" |[[File:DALL·E 2023-10-15 05.28.43 - Photo of senescent cells magnified under a microscope, showing their characteristic enlarged and flattened morphology. The cells are stained with a bl.png|frameless|75x75px]] | ||
|[[Senescent Cells|'''Cellular senescence''']] | | style="background-color:hsla(30, 100%, 75%);" |[[Senescent Cells|'''Cellular senescence''']] | ||
| Accumulation of non-dividing, dysfunctional cells secreting harmful factors. | | style="background-color:hsla(30, 100%, 75%);" |Accumulation of non-dividing, dysfunctional cells secreting harmful factors. | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style="text-align:center;" |[[File:Stem cell differentiation.svg|frameless|106x106px]] | | style="text-align:center;" |[[File:Stem cell differentiation.svg|frameless|106x106px]] | ||
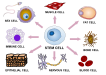
|'''Stem cell exhaustion''' | | style="background-color:hsla(30, 100%, 75%);" |'''Stem cell exhaustion''' | ||
| Decline in the regenerative capacity of stem cells affecting tissue repair. | | style="background-color:hsla(30, 100%, 75%);" |Decline in the regenerative capacity of stem cells affecting tissue repair. | ||
| rowspan="5" |'''Integrative Hallmarks''' | | rowspan="5" |'''Integrative Hallmarks''' | ||
(culprits of the phenotype) | (culprits of the phenotype) | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style="text-align:center;" | | | style="text-align:center;" | | ||
|'''Altered intercellular communication''' | | style="background-color:hsla(30, 100%, 75%);" |'''Altered intercellular communication''' | ||
| Changes in cellular communication leading to inflammation and tissue dysfunction. | | style="background-color:hsla(30, 100%, 75%);" |Changes in cellular communication leading to inflammation and tissue dysfunction. | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style="text-align:center;" |[[File:202004 Gut microbiota.svg|frameless|75x75px]] | | style="text-align:center;" |[[File:202004 Gut microbiota.svg|frameless|75x75px]] | ||
|'''Microbiome disturbance''' | | style="background-color:hsla(30, 100%, 75%);" |'''Microbiome disturbance''' | ||
'''(Dysbiosis)''' | '''(Dysbiosis)''' | ||
|Changes in gut microbiome affecting health and aging. | | style="background-color:hsla(30, 100%, 75%);" |Changes in gut microbiome affecting health and aging. | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style="text-align:center;" |[[File:Histopathology of acute and chronic inflammation of the gastro-esophageal junction, annotated.jpg|frameless|75x75px]] | | style="text-align:center;" |[[File:Histopathology of acute and chronic inflammation of the gastro-esophageal junction, annotated.jpg|frameless|75x75px]] | ||
|'''Inflammation''' | | style="background-color:hsla(30, 100%, 75%);" |'''Inflammation''' | ||
'''(Inflammaging)''' | '''(Inflammaging)''' | ||
|Systemic inflammation contributing to aging and related diseases. | | style="background-color:hsla(30, 100%, 75%);" |Systemic inflammation contributing to aging and related diseases. | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style="text-align:center;" |[[File:Cell structure (13080952404).jpg|frameless|99x99px]] | | style="text-align:center;" |[[File:Cell structure (13080952404).jpg|frameless|99x99px]] | ||
|'''Altered mechanical properties''' | | style="background-color:hsla(30, 100%, 75%);" |'''Altered mechanical properties''' | ||
|Changes in cellular and extracellular structure affecting tissue function. | | style="background-color:hsla(30, 100%, 75%);" |Changes in cellular and extracellular structure affecting tissue function. | ||
|} | |} | ||
==History== | ==History== | ||
Revision as of 10:26, 2 January 2024
Aging is characterized by a progressive loss of physiological integrity, leading to impaired function and increased vulnerability to death. The hallmarks of aging are the types of biochemical changes that occur in all organisms that experience biological aging and lead to a progressive loss of physiological integrity, impaired function and, eventually, death. They were first listed in a landmark paper in 2013[1] to conceptualize the essence of biological aging and its underlying mechanisms.
Criteria
Each hallmark was chosen to try to fulfill the following criteria:[1]
- manifests during normal aging;
- experimentally increasing it accelerates aging;
- experimentally amending it slows the normal aging process and increases healthy lifespan.
These conditions are met to different extents by each of these hallmarks. The last criterion is not present in many of the hallmarks, as science has not yet found feasible ways to amend these problems in living organisms.
Overview
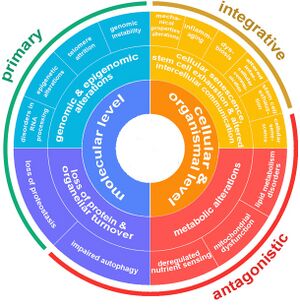
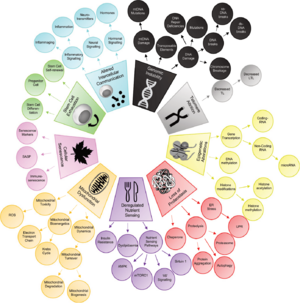
Aging is a complex process characterized by a gradual decline in physiological function. The hallmarks of aging are classified into three categories, each describing different aspects of the aging process:
- Primary Hallmarks: These are considered the main causes of cellular damage leading to aging. They are the initiating factors that, over time, drive the functional decline seen in aging cells and tissues.
- Antagonistic Hallmarks: These hallmarks are the response to the damage caused by the primary hallmarks. Initially, they may be compensatory or protective, but when chronic or excessive, they become deleterious, contributing to the aging process.
- Integrative Hallmarks: These hallmarks are the culprits of the phenotype of aging. They result from a combination of the primary and antagonistic hallmarks and are ultimately responsible for the functional decline in tissues and organs seen in aging.
The Nine Hallmarks of Aging (2013)
In the first paper in 2013[1], the following 9 landmarks of again were defined.
| # | Hallmark | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Genomic Instability | Primary Hallmarks
(causes damage) |
| 2 | Telomere Attrition | |
| 3 | Epigenetic Alterations | |
| 4 | Loss of Proteostasis | |
| 5 | Deregulated Nutrient Sensing | Antagonistic Hallmarks
(responses to damage) |
| 6 | Mitochondrial Dysfunction | |
| 7 | Cellular Senescence | |
| 8 | Stem Cell Exhaustion | Integrative Hallmarks
(culprits of the phenotype) |
| 9 | Altered Intercellular Communication |
The 14 Hallmarks of Aging (2022)
The nine hallmarks of aging, originally conceptualized by López-Otín and colleagues in 2013, have served as a foundational paradigm for aging research. While these nine hallmarks have significantly advanced our understanding of aging and its relation to age-related diseases, recent critiques and evolving scientific evidence have prompted the scientific community to reconsider and expand this framework.[4]
To address this, a symposium titled “New Hallmarks of Ageing” was held in Copenhagen on March 2022, where leading experts gathered to discuss potential additions and recontextualizations of these aging hallmarks. The symposium highlighted the critical need for an expanded, inclusive paradigm that encompasses newly identified processes contributing to aging. The discussions suggested the integration of five additional hallmarks such as compromised autophagy, dysregulation in RNA splicing, inflammation, loss of cytoskeleton integrity, and disturbance of the microbiome. These potential new hallmarks, along with the original nine, underscore a more comprehensive understanding of the aging process, acknowledging its multifaceted nature and its profound implications for human health and longevity.[5]
| Hallmark | Description | Category | Level | |
|---|---|---|---|---|

|
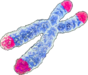
Genomic instability | Accumulation of DNA damage over time leading to cellular dysfunction. | Primary Hallmarks
(causes damage) |
Molecular |
|
Telomere attrition | Reduction in the length of telomeres leading to cellular aging. | ||

|
Epigenetic alterations | Changes in DNA methylation and histone modification affecting gene expression. | ||

|
Splicing dysregulation
(Dysregulation in RNA splicing) |
Impaired RNA construction from DNA, leading to cellular dysfunction. | ||
|
Loss of proteostasis | Disruption in protein folding and stability leading to cell damage. | ||

|
Compromised autophagy | Impaired cellular maintenance through the consumption of own components. | Antagonistic Hallmarks
(responses to damage) | |

|
Deregulated nutrient sensing | Alterations in nutrient sensing pathways affecting metabolism and aging. | Cellular & Organismal | |
|
Mitochondrial dysfunction | Decrease in mitochondrial efficiency and increase in oxidative stress. | ||

|
Cellular senescence | Accumulation of non-dividing, dysfunctional cells secreting harmful factors. | ||
|
Stem cell exhaustion | Decline in the regenerative capacity of stem cells affecting tissue repair. | Integrative Hallmarks
(culprits of the phenotype) | |
| Altered intercellular communication | Changes in cellular communication leading to inflammation and tissue dysfunction. | |||
|
Microbiome disturbance
(Dysbiosis) |
Changes in gut microbiome affecting health and aging. | ||

|
Inflammation
(Inflammaging) |
Systemic inflammation contributing to aging and related diseases. | ||

|
Altered mechanical properties | Changes in cellular and extracellular structure affecting tissue function. |
History
- 2013 The scientific journal Cell published the article "The Hallmarks of Aging", that was translated to several languages and determined the directions of many studies.[1]
- 2022 It was proposed to expand the list of the nine hallmarks of aging with five more.[5][6]
- 2023 In a paywalled review, the authors of a heavily cited paper on the hallmarks of aging update the set of proposed hallmarks after a decade.[7] A review with overlapping authors merge or link various hallmarks of cancer with those of aging.[8]
Todo
- 2013, The hallmarks of aging [1]
- 2023, Chronic inflammation and the hallmarks of aging [9]
- 2023, Aging Hallmarks and Progression and Age-Related Diseases: A Landscape View of Research Advancement [2]
- 2022, Biological mechanisms of aging predict age-related disease co-occurrence in patients [3]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 López-Otín C et al.: The hallmarks of aging. Cell 2013. (PMID 23746838) [PubMed] [DOI] [Full text] Aging is characterized by a progressive loss of physiological integrity, leading to impaired function and increased vulnerability to death. This deterioration is the primary risk factor for major human pathologies, including cancer, diabetes, cardiovascular disorders, and neurodegenerative diseases. Aging research has experienced an unprecedented advance over recent years, particularly with the discovery that the rate of aging is controlled, at least to some extent, by genetic pathways and biochemical processes conserved in evolution. This Review enumerates nine tentative hallmarks that represent common denominators of aging in different organisms, with special emphasis on mammalian aging. These hallmarks are: genomic instability, telomere attrition, epigenetic alterations, loss of proteostasis, deregulated nutrient sensing, mitochondrial dysfunction, cellular senescence, stem cell exhaustion, and altered intercellular communication. A major challenge is to dissect the interconnectedness between the candidate hallmarks and their relative contributions to aging, with the final goal of identifying pharmaceutical targets to improve human health during aging, with minimal side effects.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Tenchov R et al.: Aging Hallmarks and Progression and Age-Related Diseases: A Landscape View of Research Advancement. ACS Chem Neurosci 2023. (PMID 38095562) [PubMed] [DOI] Aging is a dynamic, time-dependent process that is characterized by a gradual accumulation of cell damage. Continual functional decline in the intrinsic ability of living organisms to accurately regulate homeostasis leads to increased susceptibility and vulnerability to diseases. Many efforts have been put forth to understand and prevent the effects of aging. Thus, the major cellular and molecular hallmarks of aging have been identified, and their relationships to age-related diseases and malfunctions have been explored. Here, we use data from the CAS Content Collection to analyze the publication landscape of recent aging-related research. We review the advances in knowledge and delineate trends in research advancements on aging factors and attributes across time and geography. We also review the current concepts related to the major aging hallmarks on the molecular, cellular, and organismic level, age-associated diseases, with attention to brain aging and brain health, as well as the major biochemical processes associated with aging. Major age-related diseases have been outlined, and their correlations with the major aging features and attributes are explored. We hope this review will be helpful for apprehending the current knowledge in the field of aging mechanisms and progression, in an effort to further solve the remaining challenges and fulfill its potential.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Fraser HC et al.: Biological mechanisms of aging predict age-related disease co-occurrence in patients. Aging Cell 2022. (PMID 35259281) [PubMed] [DOI] [Full text] Genetic, environmental, and pharmacological interventions into the aging process can confer resistance to multiple age-related diseases in laboratory animals, including rhesus monkeys. These findings imply that individual mechanisms of aging might contribute to the co-occurrence of age-related diseases in humans and could be targeted to prevent these conditions simultaneously. To address this question, we text mined 917,645 literature abstracts followed by manual curation and found strong, non-random associations between age-related diseases and aging mechanisms in humans, confirmed by gene set enrichment analysis of GWAS data. Integration of these associations with clinical data from 3.01 million patients showed that age-related diseases associated with each of five aging mechanisms were more likely than chance to be present together in patients. Genetic evidence revealed that innate and adaptive immunity, the intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway and activity of the ERK1/2 pathway were associated with multiple aging mechanisms and diverse age-related diseases. Mechanisms of aging hence contribute both together and individually to age-related disease co-occurrence in humans and could potentially be targeted accordingly to prevent multimorbidity.
- ↑ Gems D & de Magalhães JP: The hoverfly and the wasp: A critique of the hallmarks of aging as a paradigm. Ageing Res Rev 2021. (PMID 34271186) [PubMed] [DOI] [Full text] With the goal of representing common denominators of aging in different organisms López-Otín et al. in 2013 described nine hallmarks of aging. Since then, this representation has become a major reference point for the biogerontology field. The template for the hallmarks of aging account originated from landmark papers by Hanahan and Weinberg (2000, 2011) defining first six and later ten hallmarks of cancer. Here we assess the strengths and weaknesses of the hallmarks of aging account. As a checklist of diverse major foci of current aging research, it has provided a useful shared overview for biogerontology during a time of transition in the field. It also seems useful in applied biogerontology, to identify interventions (e.g. drugs) that impact multiple symptomatic features of aging. However, while the hallmarks of cancer provide a paradigmatic account of the causes of cancer with profound explanatory power, the hallmarks of aging do not. A worry is that as a non-paradigm the hallmarks of aging have obscured the urgent need to define a genuine paradigm, one that can provide a useful basis for understanding the mechanistic causes of the diverse aging pathologies. We argue that biogerontology must look and move beyond the hallmarks to understand the process of aging.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Schmauck-Medina T et al.: New hallmarks of ageing: a 2022 Copenhagen ageing meeting summary. Aging (Albany NY) 2022. (PMID 36040386) [PubMed] [DOI] [Full text] Genomic instability, telomere attrition, epigenetic alterations, mitochondrial dysfunction, loss of proteostasis, deregulated nutrient-sensing, cellular senescence, stem cell exhaustion, and altered intercellular communication were the original nine hallmarks of ageing proposed by López-Otín and colleagues in 2013. The proposal of these hallmarks of ageing has been instrumental in guiding and pushing forward research on the biology of ageing. In the nearly past 10 years, our in-depth exploration on ageing research has enabled us to formulate new hallmarks of ageing which are compromised autophagy, microbiome disturbance, altered mechanical properties, splicing dysregulation, and inflammation, among other emerging ones. Amalgamation of the 'old' and 'new' hallmarks of ageing may provide a more comprehensive explanation of ageing and age-related diseases, shedding light on interventional and therapeutic studies to achieve healthy, happy, and productive lives in the elderly.
- ↑ Researchers Propose Five New Hallmarks of Aging, https://www.lifespan.io/news/researchers-propose-five-new-hallmarks-of-aging/
- ↑ López-Otín C et al.: Hallmarks of aging: An expanding universe. Cell 2023. (PMID 36599349) [PubMed] [DOI] Aging is driven by hallmarks fulfilling the following three premises: (1) their age-associated manifestation, (2) the acceleration of aging by experimentally accentuating them, and (3) the opportunity to decelerate, stop, or reverse aging by therapeutic interventions on them. We propose the following twelve hallmarks of aging: genomic instability, telomere attrition, epigenetic alterations, loss of proteostasis, disabled macroautophagy, deregulated nutrient-sensing, mitochondrial dysfunction, cellular senescence, stem cell exhaustion, altered intercellular communication, chronic inflammation, and dysbiosis. These hallmarks are interconnected among each other, as well as to the recently proposed hallmarks of health, which include organizational features of spatial compartmentalization, maintenance of homeostasis, and adequate responses to stress.
- ↑ López-Otín C et al.: Meta-hallmarks of aging and cancer. Cell Metab 2023. (PMID 36599298) [PubMed] [DOI] Both aging and cancer are characterized by a series of partially overlapping "hallmarks" that we subject here to a meta-analysis. Several hallmarks of aging (i.e., genomic instability, epigenetic alterations, chronic inflammation, and dysbiosis) are very similar to specific cancer hallmarks and hence constitute common "meta-hallmarks," while other features of aging (i.e., telomere attrition and stem cell exhaustion) act likely to suppress oncogenesis and hence can be viewed as preponderantly "antagonistic hallmarks." Disabled macroautophagy and cellular senescence are two hallmarks of aging that exert context-dependent oncosuppressive and pro-tumorigenic effects. Similarly, the equivalence or antagonism between aging-associated deregulated nutrient-sensing and cancer-relevant alterations of cellular metabolism is complex. The agonistic and antagonistic relationship between the processes that drive aging and cancer has bearings for the age-related increase and oldest age-related decrease of cancer morbidity and mortality, as well as for the therapeutic management of malignant disease in the elderly.
- ↑ Baechle JJ et al.: Chronic inflammation and the hallmarks of aging. Mol Metab 2023. (PMID 37329949) [PubMed] [DOI] [Full text] BACKGROUND: Recently, the hallmarks of aging were updated to include dysbiosis, disabled macroautophagy, and chronic inflammation. In particular, the low-grade chronic inflammation during aging, without overt infection, is defined as "inflammaging," which is associated with increased morbidity and mortality in the aging population. Emerging evidence suggests a bidirectional and cyclical relationship between chronic inflammation and the development of age-related conditions, such as cardiovascular diseases, neurodegeneration, cancer, and frailty. How the crosstalk between chronic inflammation and other hallmarks of aging underlies biological mechanisms of aging and age-related disease is thus of particular interest to the current geroscience research. SCOPE OF REVIEW: This review integrates the cellular and molecular mechanisms of age-associated chronic inflammation with the other eleven hallmarks of aging. Extra discussion is dedicated to the hallmark of "altered nutrient sensing," given the scope of Molecular Metabolism. The deregulation of hallmark processes during aging disrupts the delicate balance between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory signaling, leading to a persistent inflammatory state. The resultant chronic inflammation, in turn, further aggravates the dysfunction of each hallmark, thereby driving the progression of aging and age-related diseases. MAIN CONCLUSIONS: The crosstalk between chronic inflammation and other hallmarks of aging results in a vicious cycle that exacerbates the decline in cellular functions and promotes aging. Understanding this complex interplay will provide new insights into the mechanisms of aging and the development of potential anti-aging interventions. Given their interconnectedness and ability to accentuate the primary elements of aging, drivers of chronic inflammation may be an ideal target with high translational potential to address the pathological conditions associated with aging.
